Assertions
Since v2.30.0
Assertion Modes
Assertion modes only apply to steps that perform assertions.
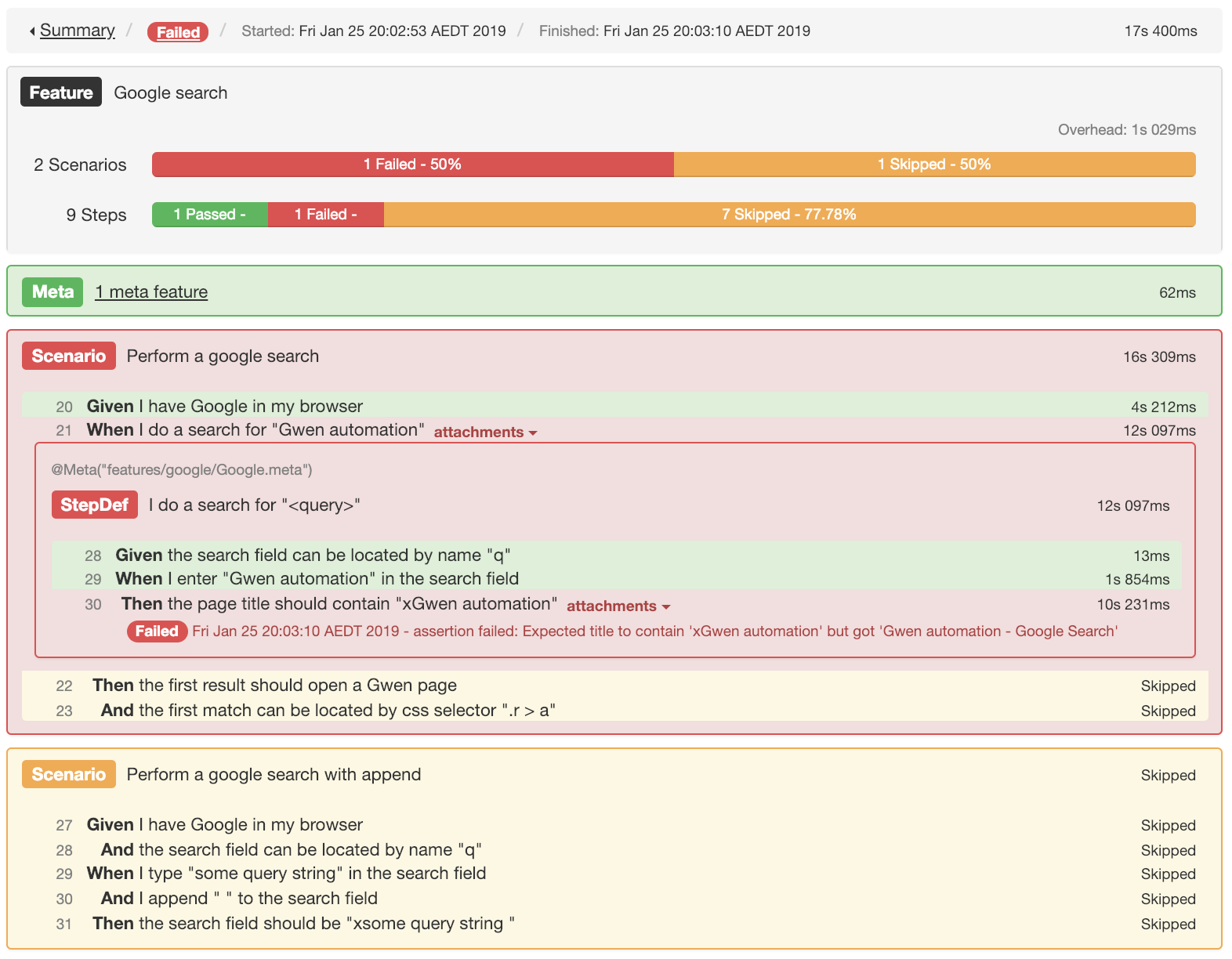
Hard assertions (default)
With hard assertions, the first assertion error to be detected will be reported as a failure and execution will halt.
Since v3.43.0, the
@Hardannotation can be used on any assertion step to make it fail hard.
Then @Hard the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
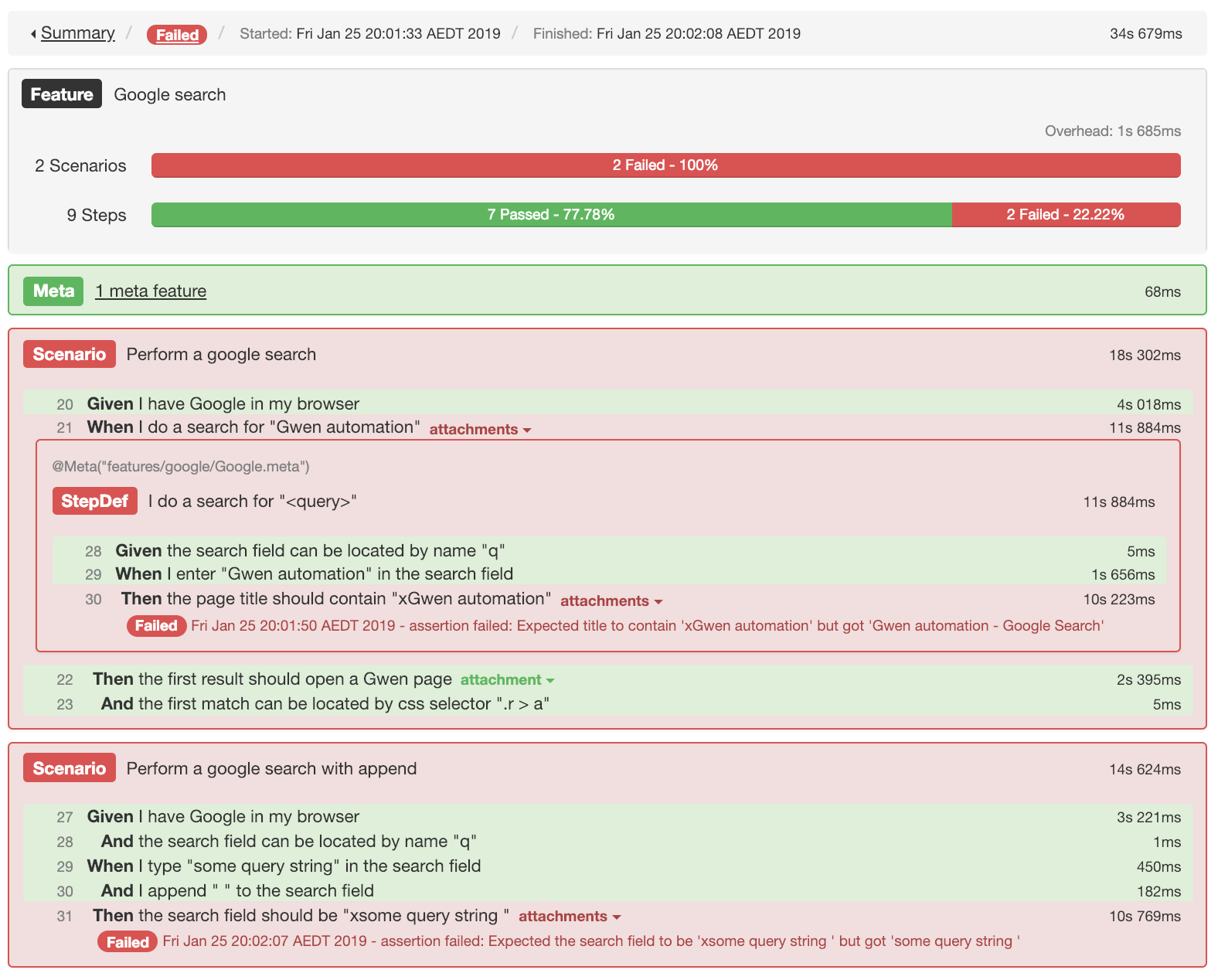
Soft assertions
With soft assertions, every assertion error that is detected is collected and reported as a failure without halting execution.
Since v3.43.0, the
@Softannotation can be used on any assertion step to make it fail soft.
Then @Soft the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
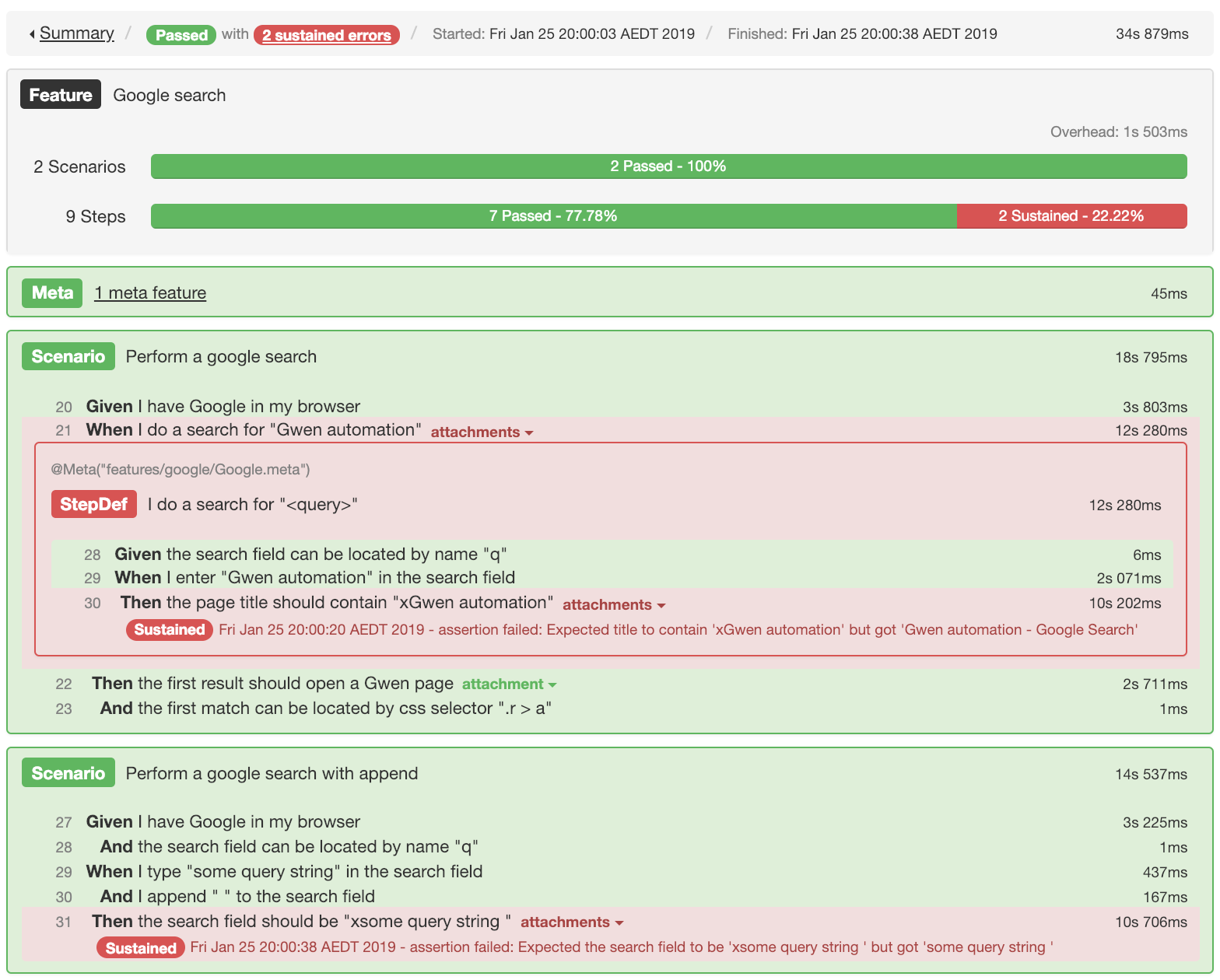
Sustained assertions
With sustained assertions, every assertion error that is detected is collected and reported as a sustained errWithout halting execution or raising failure.
Since v3.43.0, the
@Sustainedannotation can be used on any assertion step to make it sustained.
Then @Sustained the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
Default mode
Hard, soft, or sustained assertions can be configured as the default through the following setting:
gwen.assertion.mode- This setting controls whether or not hard, soft or sustained assertions are enabled by default. Valid values include:
hardto halt execution on first assertion error and report failure (default)softto collect all assertion errors and continue execution whilst reporting them as failuressustainedto collect all assertion errors and continue execution without reporting them as failures
- This setting controls whether or not hard, soft or sustained assertions are enabled by default. Valid values include:
Mode annotations
The @Hard, @Soft and @Sustained annotations introduced in v3.43.0 can be used on individiual steps to override the default assertion mode setting.
For example, if the gwen.assertion.mode setting is set to hard, the following would perform a hard assertion since no overriding annotation is specified.
Then the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
The following would also perform a hard assertion since the @Hard annotatation is explicitly specified (although redundant).
Then @Hard the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
The following however, would perform a soft assertion since the @Soft annotatation is specified.
Then @Soft the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
Similarly, the following would perform a sustained assertion since the @Sustained annotatation is specified.
Then @Sustained the page title should contain "xGwen automation"
Message Annotation
Since v3.29.0
@Message annotations can be used to override default error messages reported by failed assertions with custom messages to provide better meaning and context.
Example
Consider the following which checks that a form error should not be displayed on a page.
Given form error can be located by css `.form-error`
Then form error should not be displayed
The assertion on line 2 will fail and report the following message if the error is displayed:
assertion failed: form error should not be displayed
The default message suggests that an error was displayed but it does not explain what the error was. To override this and provide a more informative message, add a @Message annotation to the assertion as follows:
Given form error can be located by css `.form-error`
Then form error should not be displayed @Message("Form error was: ${form error}")
This will now output a more meaninful error and include the contents of the form error in it too.
- Example:
Form error was: Please provide all mandatory fields
Cumulative Assertions
Since v3.61.0
Error messages raised by a series soft or sustained assertions can be aggregated into a single errWith a cumulative assert.
Usage
Then @Soft x should not be blank
And @Soft y should be "1"
And @Soft z should be true
And there should be no accumulated errors
Line 4 will pass if all the preceeding assertions pass. If however, the assertions on line 1 and 3 fail (and the one on line 2 passes), then it will raise an assertion error containing the two failed messages as follows:
2 errors:
(1) x should not be blank
(2) z should be true but got false
Resetting
You can also reset accumulated errors if you need to start a new series of asserts. All currently accumulated errors will be cleared.
And I reset accumulated errors
Implicit variables
Text Form
Accumulated error messages can also be referenced through the implicit gwen.accumulated.errors variable.
Then @Soft x should not be blank
And @Soft y should be "1"
And @Soft z should be true
And errors is "${gwen.accumulated.errors}"
If the assertions on line 1 and 3 fail, errors on line 4 will contain:
2 errors:
(1) x should not be blank
(2) z should be true but got false
JSON Form
You can also reference the accumulated error messages as a JSON array through the implicit gwen.accumulated.errors:JSONArray variable. This approach is very flexible as it allows you to customise.
Then @Soft x should not be blank
And @Soft y should be "1"
And @Soft z should be true
And errors is defined by js
"""
() => {
const errorsJson = ${gwen.accumulated.errors:JSONArray}
return `${errorsJson.length} error(s) = ${errorsJson.join(', ')}`
}
"""
If the assertions on line 1 and 3 fail, gwen.accumulated.errors:JSONArray will resolve to:
["x should not be blank","z should be true but got false"]
And errors will evaluate to:
2 error(s) = x should not be blank, z should be true but got false
You could also use it to get the number of errors as follows:
And error count is defined by js "${gwen.accumulated.errors:JSONArray}.length"
This error count expression would evaluate to 2 in this example.